Ohio
Taxation
The state income tax was enacted in 1972. The nine-bracket schedule is adjusted yearly for inflation. For 2002, the personal income tax rates ranged from 0.743% (up to $5,000 of taxable income) to 7.5% (above $200,000). Rates for each tax year are determined in July. The corporate income tax rate is 5.1%, and 8.5% on funds over $50,000.The state sales and use tax, 5% on retail sales (excepting groceries and prescription drugs), rental of personal property, and selected services, was raised temporarily to 6%, effective 1 July 2003. A number of personal services (like dry-cleaning and hair cutting), previously untaxed, were added to the sales tax base as of 1 August 2003. Telecommunications services are scheduled to be taxed from 1 January 2004. Ohio's cities, counties, villages and school districts can impose sales taxes, and local taxes add 0.25% to 2% to the state rate. The state also collects excise taxes on motor fuels, tobacco products, insurance premiums, public utilities, alcoholic beverages, and pari-mutuels. In 2002, Ohio was one of 20 states to raise its cigarette tax, and one of seven to more that double it, going from 24 cents a pack to 55 cents a pack. The public utility excise tax, on intrastate business receipts of public utilities, is 4.75% for most utilities. The state also imposes taxes on estates (of 3% to 7% of assets over $45,000), which is independent of the federal tax exemption for state death taxes, and so not affected by the scheduled phase out of this exemption by 2007. Each estate receives a tax credit, which was $13,900 for deaths in 2002. Death and gift taxes accounted for 0.6% of state taxes collected in 2002. Other state taxes include a resources severance tax, and various license fees. The state collects just over half (54.3% in 2000) of total state and local revenues.
The state collected $19.616 billion in taxes in 2002 (down about $1.4 million from 2001), of which 42.5% came from individual income taxes, 32.6% came from the general sales tax, 12.35% from selective sales taxes, 8% from license fees, and 3.8% from corporate income taxes. In 2003, Ohio ranked 10th among the states in terms of combined state and local tax burden, which amounted to about 10.3% of income.
The following table from the US Census Bureau provides a summary of taxes collected by the state in 2002.
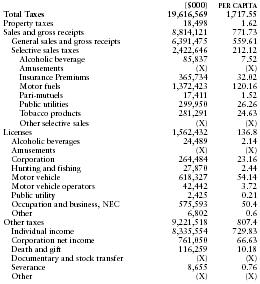
| ($000) | PER CAPITA | |
| Total Taxes | 19,616,569 | 1,717.55 |
| Property taxes | 18,498 | 1.62 |
| Sales and gross receipts | 8,814,121 | 771.73 |
| General sales and gross receipts | 6,391,475 | 559.61 |
| Selective sales taxes | 2,422,646 | 212.12 |
| Alcoholic beverage | 85,837 | 7.52 |
| Amusements | (X) | (X) |
| Insurance Premiums | 365,734 | 32.02 |
| Motor fuels | 1,372,423 | 120.16 |
| Pari-mutuels | 17,411 | 1.52 |
| Public utilities | 299,950 | 26.26 |
| Tobacco products | 281,291 | 24.63 |
| Other selective sales | (X) | (X) |
| Licenses | 1,562,432 | 136.8 |
| Alcoholic beverages | 24,489 | 2.14 |
| Amusements | (X) | (X) |
| Corporation | 264,484 | 23.16 |
| Hunting and fishing | 27,870 | 2.44 |
| Motor vehicle | 618,327 | 54.14 |
| Motor vehicle operators | 42,442 | 3.72 |
| Public utility | 2,425 | 0.21 |
| Occupation and business, NEC | 575,593 | 50.4 |
| Other | 6,802 | 0.6 |
| Other taxes | 9,221,518 | 807.4 |
| Individual income | 8,335,554 | 729.83 |
| Corporation net income | 761,050 | 66.63 |
| Death and gift | 116,259 | 10.18 |
| Documentary and stock transfer | (X) | (X) |
| Severance | 8,655 | 0.76 |
| Other | (X) | (X) |