Ohio
Languages
Ohio English reflects three post-Revolutionary migration paths. Into the Western Reserve south of Lake Erie came Northern speech from New York and Connecticut. Still common there are the Northern pronunciation of the ow diphthong, as in cow, with a beginning like the /ah/ vowel in father, and the use of the /ah/ in fog and college; /krik/ is more common than /kreek/ for creek . A dragonfly is a devil's darning needle; doughnuts may be fried cakes; a boy throws himself face down on a sled in a bellyflop (per); and a tied and filled bedcover is a comforter.
Most of nonurban Ohio has North Midland speech from Pennsylvania. Generally, except in the northern strip, cot and caught are sound-alikes, and now is /naow/, south of Columbus, because of the influence of South Midland patterns from Kentucky and extreme southern Pennsylvania, corn bread may be corn pone, lima beans are butter beans, and a tied quilt is a comforter . Spouting, yielding to gutters, barely reaches across to Indiana; and sick at the stomach, dived, and wait on me are competing with expanding Northern to the stomach, dove, and wait for me . A new Midland term, bellybuster, originated around Wheeling and has spread north to compete with bellyflop . Northern and Midland merge in the mixed dialect west of Toledo.
From Kentucky, South Midland speakers took you-all into Ohio River towns, and in the southwestern tip of the state can be heard their evening for afternoon, terrapin for tortoise, and frogstool for toadstool . Recent northward migration has introduced South Midland speech and black English, a southern dialect, into such industrial centers as Cleveland, Toledo, and Akron.
Localisms have developed. For the grass strip between sidewalk and street, Akron has devil-strip and Cleveland has treelawn . Foreign-language influence appears in such Pennsylvania Germanisms as clook (hatching hen), snits (dried apples), smearcase (cottage cheese), and got awake .
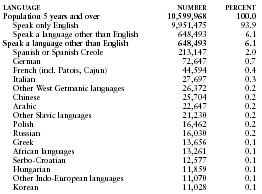
Of Ohioans aged five years or older 93.9% spoke only English at home in 2000, down from 94.6% in 1990.
The following table gives selected statistics from the 2000 census for language spoken at home by persons five years old and over. The category "Other West Germanic languages" includes Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch, and Afrikaans. The category "Other Slavic languages" includes Czech, Slovak, and Ukrainian. The category "African languages" includes Amharic, Ibo, Twi, Yoruba, Bantu, Swahili, and Somali. The category "Other Indo-European languages" includes Albanian, Gaelic, Lithuanian, and Rumanian.
| LANGUAGE | NUMBER | PERCENT |
| Population 5 years and over | 10,599,968 | 100.0 |
| Speak only English | 9,951,475 | 93.9 |
| Speak a language other than English | 648,493 | 6.1 |
| Speak a language other than English | 648,493 | 6.1 |
| Spanish or Spanish Creole | 213,147 | 2.0 |
| German | 72,647 | 0.7 |
| French (incl. Patois, Cajun) | 44,594 | 0.4 |
| Italian | 27,697 | 0.3 |
| Other West Germanic languages | 26,372 | 0.2 |
| Chinese | 25,704 | 0.2 |
| Arabic | 22,647 | 0.2 |
| Other Slavic languages | 21,230 | 0.2 |
| Polish | 16,462 | 0.2 |
| Russian | 16,030 | 0.2 |
| Greek | 13,656 | 0.1 |
| African languages | 13,261 | 0.1 |
| Serbo-Croatian | 12,577 | 0.1 |
| Hungarian | 11,859 | 0.1 |
| Other Indo-European languages | 11,070 | 0.1 |
| Korean | 11,028 | 0.1 |